Do you think building apps is just for developers? Not anymore. Thanks to low-code platforms like Power Apps, anyone- even without coding experience- can create business apps. That’s where citizen developers come in.
Power platform citizen developers use PowerApps to solve everyday challenges, automate tasks, and streamline workflows – without waiting on IT. Whether it’s an HR pro tracking job applications or a sales team managing leads, low-code citizen developers are making work easier and faster.

This isn’t just a trend; it’s the future. Businesses that embrace PowerApps citizen development are cutting costs, boosting innovation, and staying ahead of the game. Let’s explore why a low-code strategy is a must for every enterprise navigating through citizen development.
Table of Contents
What Do Power Platform Citizen Developers Do?
Why Enterprises Need a Low-Code Strategy?
How Does Power Apps Support Citizen Development?
Common Power Apps Development Challenges and How to Overcome Them
What is Citizen Development?
Citizen development enables non-technical employees to develop apps without coding through low-code or no-code platforms. These platforms provide drag-and-drop features and pre-existing templates. This is convenient when designing, testing, and deploying applications.
Citizen development enables companies to work more quickly. It minimizes the use of professional developers for basic projects and helps professionals in other domains develop suitable tools. This is time-saving and efficient. Various industries, such as healthcare, finance, and retail, employ citizen developers to enhance operations.
What Do Power Platform Citizen Developers Do?
Power platform citizen developers are employees who build apps without formal programming skills. They employ low-code or no-code tools to develop solutions for their everyday tasks. Their primary goal is to resolve business issues on time.
They automate manual processes to save time. For example, a PowerApps citizen developer in HR may create an app to track job applications. In sales, they might build a tool to manage customer data.
PowerApps citizen developers also improve teamwork. They make apps that help teams share information and work better together. Since they understand their department’s needs, they create solutions that fit well.
Security is important in citizen development. Citizen developers follow company rules to keep data safe. IT teams often guide them to ensure security and quality.
As technology grows, low-code citizen development will become even more popular. More companies will train employees to create solutions. This will lead to faster growth and better business results.
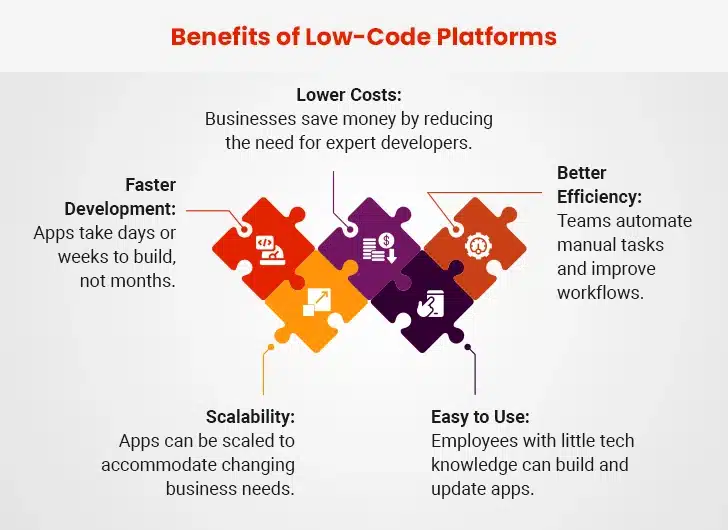
What are Low-Code Platforms?
Low-code platforms help people build software with little coding, reducing the need for professional developers.
These platforms have simple interfaces. Users drag elements like buttons and forms onto a screen. They also connect apps to databases, websites, and other software.
Most platforms offer ready-made templates. These help low-code citizen developers start projects without building everything from scratch. Some platforms also have AI-powered tools that suggest further improvements.
Who Uses Low-Code Platforms?
Many industries use low-code platforms. Banks create customer service apps. Hospitals build patient tracking systems. Retailers use them for inventory management. Even schools use them to manage student records.
Low-code tools help businesses of all sizes. Small companies use them to build cost-effective solutions. Bigger companies use them to speed up innovation.
However, low-code citizen developers often face challenges with customization. Low-code tools work well for simple apps but may not suit complex needs. Businesses may still need professional developers for advanced features.
Why Enterprises Need a Low-Code Strategy?
1. Faster Application Development
Traditional app development takes months or even years. Low-code platforms speed up the process with drag-and-drop tools and pre-built templates. Teams build applications quickly without writing long lines of code. Businesses respond to market changes faster and stay ahead of competitors.
Instead of waiting for developers, employees create solutions themselves. This leads to shorter project timelines and quicker problem-solving. Faster development improves efficiency across departments.
2. Reduced IT Dependency
Most businesses rely on IT teams for software development. However, IT departments often face large workloads and resource limitations. A low-code strategy helps by allowing employees outside IT department to build applications. Business users create solutions without technical expertise.
Departments like sales, HR, and finance develop apps that improve workflow. IT teams still oversee security and compliance but do not have to handle every request. Reduced IT dependency leads to faster innovation across the organization.
3. Lower Development Costs
Hiring professional developers and maintaining complex software is expensive. A low-code strategy helps reduce costs by allowing existing employees to create applications. Through this strategy, businesses avoid large investments in custom software and spend less on third-party development services.
Since low-code platforms provide pre-built components, companies do not need to build apps from scratch. Maintenance costs are lower because employees update and manage apps without external help. Businesses allocate saved resources to other critical areas. Small and medium-sized companies benefit the most by reducing software expenses. A low-code strategy makes technology development more affordable and accessible.
4. Better Collaboration Between Teams
A low-code strategy brings business and IT teams closer. Traditionally, IT handles software development while business teams provide requirements. This separation often causes delays and misunderstandings. Low-code platforms bridge the gap by allowing both teams to work together. Business users create apps with minimal IT involvement. IT teams oversee security and technical aspects while ensuring proper functionality. Collaboration improves because employees directly build the tools they need. Workflows become smoother, and applications align better with business goals. With improved teamwork, businesses build solutions faster and more efficiently. This leads to higher productivity across the organization.
5. Enhanced Security and Compliance
A low-code strategy ensures compliance with security standards through built-in security layers. These platforms provide role-based access, data encryption, and audit trails. Businesses set permissions to control the access of sensitive information. IT teams monitor security without handling every project themselves.
Low-code platforms also follow industry regulations, ensuring data privacy. Organizations maintain control while allowing employees to build applications safely. With security features included, businesses reduce the risk of breaches.
6. Better Scalability
A low-code strategy allows organizations to build scalable apps without major redevelopment. Applications adjust to increased users, larger databases, and changing business needs. Instead of rebuilding systems from scratch, businesses update and expand existing apps. Cloud-based low-code platforms support scaling by handling more traffic and data. Companies readily add new features without affecting performance. This flexibility ensures that technology investments remain useful.
7. Higher Employee Productivity
A low-code strategy boosts productivity across all departments. According to a survey, 80% of C-suite executives believe low-code development improves the productivity of tech teams. Teams fix issues and develop solutions instead of waiting for IT support. Businesses eliminate bottlenecks that slow down operations. With easy-to-use development tools, more employees contribute to digital transformation. The result is a more efficient workforce with improved performance. A low-code strategy helps businesses achieve more with fewer resources.
Scale Your Development Process with Power Apps
How Does Power Apps Support Citizen Development?
I. No Need for Coding Knowledge
Power Apps is designed for individuals who don’t have expert coding skills. It includes a visual tool where users can design apps using a drag-and-drop interface. Instead of creating long strings of code, users select features and create easy rules. This allows HR, sales, and finance employees to build apps for their workflows easily.
Hence, companies do not have to rely on developers for minor projects. They can also update these applications quickly without waiting for the IT staff. By eliminating the requirement to code, Power Apps enables more employees to contribute to app development. This results in quicker problem-solving and increased innovation.
II. User-Friendly Interface
Power Apps has a straightforward interface that is easy for anyone to navigate. It comes with pre-built templates that make it easy for users to start development quickly. The drag-and-drop feature allows users to insert buttons, forms, and fields easily. It also comes with guides and tutorials for novices, so employees do not have to master complicated software.
Another benefit of Power Apps is that it enables users to test their apps in real-time. They can monitor the app functionalities and make immediate adjustments. Since it is easy to learn and work on, more employees can develop apps and enhance work processes.
III. Rapid App Development
Traditional app development is time-consuming, usually taking months to move from planning to deployment.
Power Apps accelerate the process of app development. Employees develop working apps within a few hours or days. It has pre-built features, meaning users do not have to begin from zero. They also do not need to wait for IT departments to develop small tools. This enables companies to work faster and adapt to new challenges. By saving time on app development, businesses remain ahead of their competition.
IV. Automation of Tasks
Most companies are still working manually, which is time-consuming and results in errors. Power Apps assists by automating approvals, reminders, and data entry.
For instance, an HR department may develop an app to process leave requests. Employees fill out forms, and managers approve them with a single click. A sales team may create an app to update customer information automatically. This eliminates the requirement for additional paperwork and data entry. Minimizing manual labor helps employees dedicate their time to more critical tasks.
V. Mobile and Web Compatibility
Power Apps-developed applications function across various devices. They operate on phones, tablets, and computers, making it easy for employees to access their applications anywhere. For example, a field technician may log service requests via a mobile application. Similarly, remote employees generate reports without using a desktop.
Applying on various platforms means employees stay connected to work and collaborate easily with their peers. This enhances flexibility and enables companies to react to demands promptly. With these apps, employees can do their jobs on the go, making processes more efficient.
VI. Enhances Team Coordination
Power Apps facilitates enhanced collaboration among teams. Employees create apps that encourage better communication and information sharing. A project team may develop an app to keep track of jobs and deadlines. A sales unit may develop an app to give customers updates. Since Power Apps is cloud-based, several individuals may use and tweak an app simultaneously.
This ensures that teams always get the latest information. It also prevents miscommunication and delays.
VII. Cost-Effective Solution
It is often costly to hire software developers, and most companies cannot afford to engage massive development teams. Power Apps saves money by allowing employees to make their own apps. Rather than having to pay for software that is made specifically for them, companies use Power Apps to fix issues.
It helps small businesses create apps without affecting their budget. On the other hand, bigger companies save on development costs and concentrate on larger projects.
Power Apps is included with Microsoft 365, so companies with Microsoft tools derive more value from their investment. This makes it a wise and cost-effective option.
VIII. Secure and Compliant
Power Apps adheres to Microsoft’s robust security guidelines. It includes capabilities such as role-based access, encryption, and data protection.
Companies have complete control on who accesses or adjusts data in an app, blocking unauthorized individuals from modifying it. Power Apps also integrates with Microsoft security components, such as Azure Active Directory, offering additional layers of security for user data. Because of these security features, companies rely on Power Apps to secure their data.
IX. Empowers Employees
Power Apps helps employees fix their problems. Rather than waiting for IT departments, they develop apps to enhance their work. For instance, a customer support representative may develop an app to monitor complaints, or a marketing team may create an app to run campaigns.
This autonomy makes employees feel more in charge of their work. It also inspires them to think creatively about problems. Employees who create the tools work more effectively, resulting in higher outcomes and greater job satisfaction.
Common Power Apps Development Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Resistance to Change
Employees might be resistant to new software. Proper training and support help employees adapt better to change. Hence, companies must hold workshops and publish easy-to-understand documentation to promote usage.
Governance and Compliance
IT groups should establish specific policies to allow safe app development. Power Apps comes with native governance capabilities to handle such issues. Organizations should institute policies to manage app creation and data access.
Scaling Beyond Basic Apps
While Power Apps is wonderful for small applications, more sophisticated projects require IT help. IT staff and Power Platform citizen developers must collaborate to scale solutions. Organizations must establish a center of excellence to lead developers and maintain high standards.
Conclusion
Low-code development is necessary for success in the digital age. Power Apps enables businesses to develop solutions quickly and affordably. Organizations that embrace Power Platform citizen development will remain ahead of the curve. With the right strategy, companies can unlock the maximum potential of low-code technology and drive innovation, enhance efficiency, and boost collaboration.





