Managing Google Cloud expenses can be a real challenge, especially when your projects start scaling fast and different teams spin up resources left and right. It’s easy to lose track of where your money is going, and before you know it, your cloud expenses are way higher than expected. The good news? You’re not alone.
Many businesses encounter this issue, and the solution often lies in optimizing their use of the platform. Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offers incredible flexibility and performance, but cloud costs can add up fast without the correct practices. That’s where GCP cost optimization comes into play.
This guide outlines ten practical, proven strategies for helping you use your cloud budget more intelligently. Let’s get started.

Table of Contents
Why Does GCP Cost Optimization Matter?
Key Factors That Impact Your GCP Bill
Ten Tips for Effective GCP Cost Optimization
- 1. Right-Size Your Compute Resources
- 2. Use Committed Use Discounts (CUDs)
- 3. Take Advantage of Sustained Use Discounts (SUDs)
- 4. Schedule and Automate Idle Resource Shutdowns
- 5. Use Preemptible VMs for Short-Term Workloads
- 6. Monitor and Analyze Billing with Cost Tools
- 7. Optimize Storage Usage and Lifecycle Policies
- 8. Use Labels for Better Resource Tracking and Accountability
- 9. Set Budgets and Alerts to Stay in Control
- 10. Regularly Audit and Clean Up Unused Resources
Why Does GCP Cost Optimization Matter?
GCP cost optimization is important because it helps reduce unnecessary spending and ensures efficient use of cloud resources. It helps you:
- Lower your overall cloud expenses by cutting waste
- Reallocate savings to more critical business areas
- Identify and shut down idle or underused services
- Improve system performance through smarter resource use
- Gain better visibility and control over your cloud budget
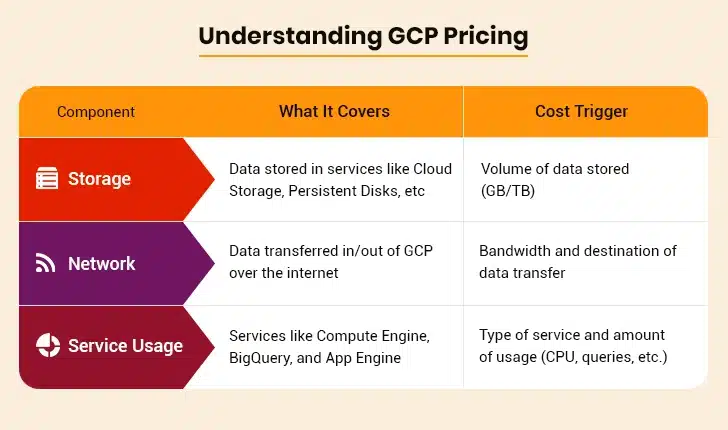
Key Factors That Impact Your GCP Bill
Here are some key factors that impact your GCP bill:
- Computer usage: It includes virtual machines, CPU hours, and machine types
- Storage consumption: Costs vary based on storage class, size, and access frequency
- Network traffic: Ingress is free, but egress adds up, especially across regions
- Data processing services: BigQuery, Dataflow, and other services are charged based on usage
- Resource provisioning: Over-provisioned or idle resources increase costs
Ten Tips for Effective GCP Cost Optimization
Whether you’re just starting your Google Cloud journey or looking to fine-tune your operations, these tips will support better GCP cost management while ensuring performance and scalability.
1. Right-Size Your Compute Resources
One of the easiest and most impactful GCP cost-saving strategies is right-sizing your compute resources. Organizations often over-provision their virtual machine (VM) requirements and pay charges for unused capacity. With GCP cost management tools, you can monitor CPU and memory usage to identify underused VMs. Once you have that data, adjust the instance type to fit your workloads better.
By right-sizing, you reduce waste and improve the overall efficiency of your cloud usage. Google Cloud Cost Management features can also recommend ideal machine types, helping you make informed decisions. It’s essential to review these insights since workloads often change over time.
In addition to VMs, consider right-sizing persistent disks and other resources. GCP cloud cost optimization depends on matching your infrastructure’s size to your applications’ demand. Whether running an app or managing data center migration, right-sizing helps you avoid the trap of over-provisioning and keeps costs predictable.
In short, paying only for what you use is key to effective GCP cost optimization. Making minor adjustments regularly results in substantial savings.
2. Use Committed Use Discounts (CUDs)
One of GCP’s most effective cost optimization strategies is applying Committed Use Discounts (CUDs). Google Cloud provides these discounts if you commit to utilizing a minimum amount of resources (such as vCPUs or memory) for one year or three years. This allows you to achieve a 57% discount over on-demand pricing and is an economical choice for fixed workloads.
This commitment can drastically lower your bill if you know that specific applications or services will run consistently over time. CUDs help with GCP cost management by converting variable spending into fixed costs, which makes budgeting easier.
It’s worth examining usage habits before committing. Google Cloud offers suggestions based on your previous usage to help you buy the correct commitment level. These tools simplify scanning your environment and taking action where necessary.
Google Cloud cost optimization isn’t just about cutting back—it’s also about spending smarter. CUDs are an ideal example of strategic planning that supports cloud cost optimization while maintaining performance. For any business with stable and long-running workloads, CUDs improve the overall return on investment (ROI) of your cloud infrastructure.
3. Take Advantage of Sustained Use Discounts (SUDs)
Sustained Use Discounts (SUDs) are another easy way to support GCP cost optimization without manual effort. Google Cloud automatically applies these discounts when you use specific resources, like Compute Engine VMs, for a significant portion of the billing month. The longer you use the resource, the higher the discount—up to 30%.
This is especially helpful for continuously running applications like backend services, databases, or internal tools. Unlike Committed Use Discounts, no upfront commitment or long-term planning is required. SUDs kick in automatically, making them a passive but effective GCP cost management feature.
To maximize SUDs, consolidate workloads onto fewer, longer-running VMs instead of many short-lived ones. This improves Google Cloud cost optimization and simplifies resource tracking and billing. SUDs apply across projects within the same billing account, so you still get the benefits if you’re managing multiple projects.
Incorporating SUDs into your GCP cloud cost optimization strategy helps ensure you’re not wasting automatic savings opportunities. Combined with other Google Cloud cost management tactics, it becomes a solid foundation for reducing unnecessary spending while keeping your systems running smoothly.
4. Schedule and Automate Idle Resource Shutdowns
One of the least addressed areas of GCP cost optimization is finding and shutting off idle resources. Virtual machines, databases, and Kubernetes clusters that are not in use but still up can quietly contribute to your bill. Manually shutting them off is an option, but automating it guarantees long-term GCP cost management.
With applications such as Google Cloud Scheduler or Cloud Functions, resources may automatically shut down or be deleted if usage ceases late in the day or slackens significantly. For example, developing script components that stop resources late evenings or on weekends would be simple if you deploy only within business hours.
This approach reduces waste and enforces better discipline in managing cloud resources. It’s a practical move that supports both Google Cloud cost optimization and operational efficiency. Google also offers Recommender, which provides automated suggestions for removing idle disks, IPs, and other unused resources.
Incorporating idle resource automation into your cloud cost optimization strategy ensures your team only pays for what they use. Monitoring and automating alerts make tracking and controlling unnecessary costs easier, strengthening your overall cloud cost management approach.
5. Use Preemptible VMs for Short-Term Workloads
Preemptible VMs are a cost-effective solution for short-lived or flexible workloads and can play a key role in GCP cost optimization. These are low-cost, short-duration virtual machines offered by Google Cloud at a significantly reduced rate, often up to 80% cheaper than regular VMs. The catch is that Google can stop them anytime, so they’re best suited for fault-tolerant jobs. If your workloads include batch processing, rendering, data analysis, or test environments, Preemptible VMs are a wise choice. They help improve GCP cost management by lowering costs without compromising processing power for tasks that can handle interruptions or be restarted.
You can also use managed instance groups to replace preempted VMs, ensuring workloads run automatically. Combining Preemptible VMs with durable storage and smart retry logic ensures your tasks can pick up where they left off without losing data or progress.
For companies with large-scale, non-critical compute needs, Preemptible VMs are a game-changer for GCP cloud cost optimization. They allow businesses to maintain performance while staying within budget, making them an essential part of a well-rounded cloud cost optimization plan that doesn’t sacrifice productivity for savings.
6. Monitor and Analyze Billing with Cost Tools
Effective GCP cost optimization starts with visibility. You can’t cut what you can’t see. Google Cloud provides natively integrated features such as the Billing dashboard, Cost Table, and Cost Breakdown, which enable you to monitor your spending in detail. These features help make GCP cost management transparent by revealing where your money goes.
Going through these reports assists in recognizing trends, spikes, and services causing unbudgeted costs. For instance, if a service or project suddenly begins taking up more resources, it is proactively detected, and you can act before it affects your budget. You can also set up budgets and alerts to notify your team when spending crosses a certain threshold.
Cost tools also allow filtering by projects, labels, and services, making it easier to track usage across teams. This level of insight supports Google Cloud cost optimization by revealing which services are used efficiently and which might be over-provisioned.
Integrating these insights into your cloud cost optimization workflow ensures that decisions are based on actual usage data. Over time, consistent monitoring becomes one of the most reliable ways to keep your Google Cloud cost management efforts on track and your cloud bills under control.
7. Optimize Storage Usage and Lifecycle Policies
Storage is usually a silent cause of escalating cloud bills, so optimizing how you store and handle data is essential for GCP cost optimization. Google Cloud has various storage classes:
- Standard
- Nearline
- Coldline
- Archive
Prices vary depending on the frequency of data access. Selecting the correct class for each data type is an easy but powerful GCP cost management strategy.
For example, frequently accessed files should be stored in Standard, while backups or rarely retrieved logs can go into Archive or Coldline storage. This tiered approach helps match storage needs with pricing, reducing unnecessary spending.
Lifecycle policies make this process easier by automatically transferring data to less expensive storage classes after some time has passed. For example, you can create a rule to transfer logs older than 30 days to Coldline. These rules are low maintenance but provide high savings in the long run.
Regular audits of storage usage are also key to GCP cloud cost optimization. Deleting obsolete data and unused buckets frees up space and reduces charges. These practices support cloud cost optimization and keep your data organized for long-term Google Cloud cost management.
Optimize Your Google Cloud Without Sacrificing Performance
8. Use Labels for Better Resource Tracking and Accountability
Applying labels to your resources is a simple yet powerful way to optimize GCP cost. Labels are key-value pairs that let you categorize resources based on projects, teams, environments, or purposes. This improves visibility, making it easier to see where your cloud budget is spent.
When used effectively, labels enhance GCP cost management by allowing you to filter costs by department, client, or workload. This helps track which teams are consuming more resources and whether that usage is justified. It also promotes accountability, as every team can see the cost impact of their work.
For example, adding labels like “env: production” or “team: marketing” helps you break down your monthly cloud spend in the billing reports. Google Cloud’s built-in cost tools fully support labeled filtering, which is helpful for both analysis and budgeting.
When it comes to Google Cloud cost optimization, labeling ensures that no cost goes unaccounted for. It also helps identify idle or orphaned resources that may be forgotten but are still generating charges. Including labels as a standard part of your deployment process supports long-term GCP cloud cost optimization and builds a more transparent Google Cloud cost management culture across teams.
9. Set Budgets and Alerts to Stay in Control
One of the most forward-thinking things you can do for GCP cost optimization is to set budgets and alerts. This way, you know how much you’re spending—and how close you are to hitting your limits. Google Cloud allows you to set budgets by project, product, or label and sends you an email when spending gets near the limit.
This offers more intelligent GCP cost management by detecting unexpected cost increases early. For instance, if a service starts consuming more resources than usual, your team receives an alert before the bill escalates. Such alerts can also initiate automated workflows, such as stopping or modifying services, to prevent additional costs.
Setting budgets is not just about limiting spending—it’s also a key part of cloud cost optimization planning. It helps align cloud use with business goals and avoids surprise expenses. This tactic is used consistently to strengthen your GCP cloud cost optimization strategy.
10. Regularly Audit and Clean Up Unused Resources
Routine cleanups are essential for effective GCP cost optimization. Over time, unused or forgotten resources—such as idle virtual machines, unattached persistent disks, unused IP addresses, or stale snapshots—can quietly blow out your cloud bill. Regular audits identify and eliminate these unnecessary items, making your system more efficient and easier to manage costs on GCP.
Google Cloud offers Recommender and the Asset Inventory API tools to identify idle or underused resources. These tools simplify the process of scanning your environment and take necessary actions.
Scheduling a monthly or quarterly check on your cloud environment ensures such costs do not accumulate over time. You can also create automated cleanup scripts or policies that automatically delete or archive resources after a specified duration.
This routine maintenance supports Google Cloud cost optimization by keeping your cloud setup lean and efficient. It also strengthens your long-term GCP cloud cost optimization practices by avoiding the habit of “set and forget.” Regular audits are one of the easiest and most reliable ways to maintain healthy Google Cloud cost management.
Conclusion
Optimizing your Google Cloud Platform (GCP) expenses doesn’t mean making drastic changes—just steady, intelligent habits. You can manage cloud spending without compromising performance by right-sizing resources, taking advantage of discounts, automating idle shutdowns, and monitoring billing.
With the proper tools and practices, cost optimization becomes more than bookkeeping—it is a competitive advantage. Start small, stay consistent, and let data guide your decisions to get the most value from your GCP investment.





