Data is at the center of every modern business. It informs decisions, fuels operations, and defines customer experiences. However, data needs to be analyzed to be used effectively, and before that, it needs to be stored and managed. That’s where enterprise data management (EDM) enters the picture. Enterprise data management is a strategic framework that involves defining, integrating, and retrieving data in an organization for internal and external processes.
A well-defined EDM system improves with time, and evaluating its maturity guarantees that it stays ahead of business demands.
Let’s understand what enterprise data entails before discussing why a data management maturity assessment is necessary for a data-driven enterprise.
Table of Contents
Enterprise Data Management Types
Aligning Enterprise Data with a Maturity-Driven Framework
What Is a Data Management Maturity Assessment?
Five Levels of Data Management Maturity
Why Does Maturity Assessment Matter?
Signs Your Business Needs a Data Maturity Assessment
- Variable Data Quality Between Departments
- Inaccessibility or Difficulty in Retrieving Data
- Data Security and Compliance Threats
- Siloed Data Creating Inefficiencies
How to Perform a Data Management Maturity Assessment
Conclusion
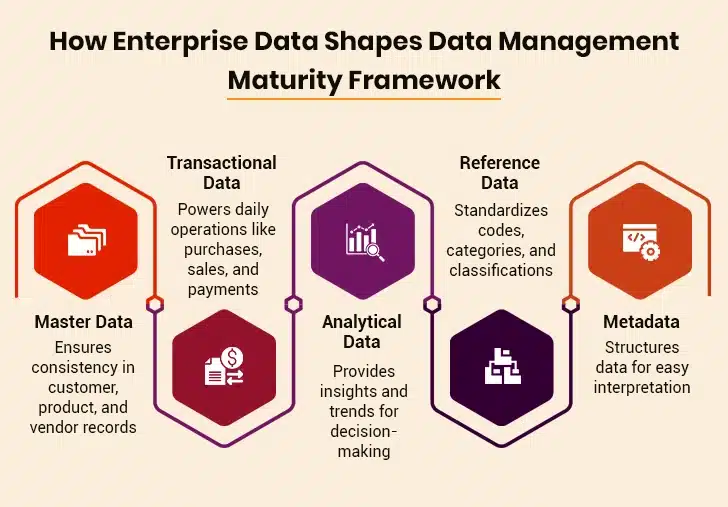
Enterprise Data Management Types
- Master Data: Master data is the standardized identifiers that define non-transactional characteristics of important business entities. It encompasses the unique aspects within domains like products, customers, and vendors. Master data, for example, contains vendor information with predetermined attributes. The vendors have a unique ID used across transactional systems for business operations to proceed.
- Transactional Data: This data contains information about key business functions and transactions. It comprises information about procurement, production, sales, and other functional activities. For example, the details of a product sale, including quantity, price, and date, are transactional data.
- Analytical Data: Also referred to as reporting data, analytical data is extracted from transactional data and used for detailed business analysis. It relies on master data to segment and analyze business performance from various points of view. Consolidating and aggregating information helps organizations derive insights that inform strategic decisions.
- Reference Data: A specialized subset of master data, reference data, offers a standardized structure for maintaining consistency throughout an organization. It is relatively stable and doesn’t frequently change. Examples include predefined lists like country names, states, and city codes, which help to ensure uniformity across systems.
- Metadata: Metadata is descriptive and structural information regarding other data, giving context to business data. For instance, an individual’s name can consist of three elements: First Name (required), Last Name (required), and Middle Name (optional). This formatted information acts as metadata, aiding in data organization and use.
By combining these different types of data, enterprise data management operates in a methodical, networked, three-layered structure to maintain data consistency, reliability, and accessibility.
Aligning Enterprise Data with a Maturity-Driven Framework
Data empowers businesses, but without proper organization, it becomes chaotic. An enterprise data management framework ensures optimum data governance, integration, and utilization.
A data management maturity assessment enhances this framework by highlighting gaps and areas of optimization. The outcome? A smooth, data-driven environment for making better decisions.
What Is a Data Management Maturity Assessment?
A data management maturity assessment is a formal process that quantifies an organization’s capacity to manage data effectively. It helps companies assess their progress in data governance, quality, security, integration, and analytics.
This evaluation employs a maturity model to rate the company’s data management processes. Thus, companies can develop a roadmap for refining and integrating their data strategy with business objectives. It also helps companies establish their strengths and weaknesses.
Five Levels of Data Management Maturity
Most maturity models categorize data management into five levels, from fundamental to sophisticated. The following is an outline of these levels:
Initial (Chaotic)
In this phase, enterprise data management is disorganized and not structured. Data is usually kept in isolated silos, and accessing and analyzing them becomes inefficient. There are no established policies regarding data governance, and inconsistencies and errors are common. Organizations at this level use manual processes and gut feelings instead of data-driven intelligence, which causes inefficiencies and higher operational risks. Businesses experience slow decision-making and unreliable data without an enterprise data management system.
Emerging (Reactive)
Some companies have started to see the value of systematic data management but continue to work with ad-hoc methods. Diverse departments manage data differently, which results in duplication and inefficiencies.
Organizations may deploy simple enterprise data management frameworks, but they do not have formal governance policies. Their security and compliance measures are weak, raising the threat of data breaches. Organizations find it difficult to ensure data consistency and reliability without a standardized enterprise data management tool.
Defined (Proactive)
At this phase, organizations have formal policies and structured procedures for data governance. An enterprise data management tool supports a centralized approach to storing and making data available.
Employees follow procedures uniformly, and businesses initiate the use of data analytics as a means of making decisions. Thus, companies benefit from employing enterprise data management services to organize workflows and de-silo data.
Managed (Advanced)
Data management is now a core business function at this level. Companies spend money on data management software that improves data quality and integration. Governance structures are robust to ensure regulatory compliance and automated processes guarantee data accuracy.
Advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are essential in business operations. Enterprise data management systems enable data sharing between departments without hindrance, allowing for better decision-making.
Maximized (Innovative)
At this stage, businesses are equipped with integrated enterprise data management systems that encourage innovation and maximization. Data is processed in real time and used in predictive analysis, giving vital information to guide decision-making. Security and compliance are intrinsic to all data management processes to prevent risk.
Enterprises periodically upgrade their data management systems to fit changing technologies and organizational needs. Data is treated as a strategic resource, helping firms advance in the competitive marketplace.
Why Does Maturity Assessment Matter?
1. Improves Data Quality and Accuracy
A maturity assessment enhances data accuracy and consistency. It detects errors, redundancies, and inconsistencies in data management. Cleaner, more accurate data enhances decision-making. An enterprise data management framework with clear definitions guarantees data integrity. Standardized processes enhance data validation and eliminate inaccurate reporting.
2. Streamlines Data Management Processes
Maturity assessment facilitates efficient data management operations. It analyzes existing processes and highlights inefficiencies in processes.
Enterprise data management tools automate maturity assessments, minimize manual interventions, and enhance data availability. An organized process makes overall data-driven decision-making more effective.
3. Enhances Regulatory Compliance and Data Governance
Maturity checks ensure alignment with industry policies and regulations. They enhance data governance in an enterprise data management strategy, avoid compliance risks, and prevent legal penalties.
Uniform data policies ensure consistency in enterprise data management tools. Better governance promotes transparency and accountability in data usage.
4. Boosts Operational Efficiency and Productivity
An organized enterprise data management system enhances business processes. Workers spend fewer hours working with redundant or incorrect information. Data-driven automation minimizes human interaction and increases efficiency.
A comprehensive data management solution simplifies repetitive data activities. Streamlined data processes drive quicker and more accurate reporting.
5. Enhances Decision-Making with Accurate Insights
Data maturity ensures that business decisions are based on correct information. An optimized data management system reduces the possibility of making bad decisions.
Good-quality data makes forecasting and planning more accurate. Organizations can trust reports based on enterprise data management applications—better data visibility results in a more innovative business strategy.
6. Supports Seamless Integration of Data Between Systems
A maturity evaluation guarantees seamless data integration among business applications. It eliminates data silos in the enterprise data management architecture.
Enterprises can use data management software for interoperability. Integrated systems enhance collaboration and increase cross-functional data sharing. Improved integration enables real-time insights and increased efficiency.
7. Improves Data Security and Risk Management
An organized maturity assessment picks out weaknesses in data security mechanisms. It promotes more effective defense within an enterprise data management environment. Companies can add data encryption and access control strategies.
Safe data management environments limit the risks of data compromise. Enhanced security helps foster customer trust and defend against sensitive information.
8. Supports Scalability and Future Data Growth
Maturity evaluations enable companies to prepare for growing data requirements. A scalable enterprise data management system can handle increasing volumes of data. Organizations no longer have to change enterprise data management applications to meet changing requirements.
Uniform data frameworks provide seamless conversions as businesses expand. Scalable data handling minimizes the overloading of systems and slowdowns.
9. Lessens the Costs of Inefficient Data Handling
Enhancing data maturity reduces costs associated with incorrect or duplicate data. An effective enterprise data management system reduces storage and processing costs. Cost savings lead to improved financial management and resource allocation.
Automated data cleansing saves time on manual correction. An adequately maintained data management system prevents data duplication.
10. Improves Customer Experience and Business Competitiveness
A data management platform provides correct customer records and customer preferences. It facilitates strong data management that results in enhanced customer intelligence and personalization. Effective data handling also supports business competitiveness within the digital business environment.
Assess Your Data Maturity Today and Unlock Hidden Business Insights
Signs Your Business Needs a Data Maturity Assessment
Variable Data Quality Between Departments
Data quality is essential for sound business decisions. If disparate departments work with inconsistent or unreliable data, it may result in expensive errors.
Data maturity analysis recognizes weaknesses in the data management system and provides solutions for maintaining data accuracy. An enterprise data management framework aligns data with all the departments.
Moreover, an enterprise data management software automatically implements data validation mechanisms, resulting in fewer human errors. Resolving data quality initially by conducting a maturity assessment helps build a reliable foundation for analytics and business intelligence.
Inaccessibility or Difficulty in Retrieving Data
If the staff members take inordinate amounts of time to locate relevant data, it indicates inefficiencies in the data management system. Delayed access to critical data can impact productivity and the speed of decision-making.
Maturity assessment pinpoints data accessibility bottlenecks and proposes enhancements. Having an enterprise data management system guarantees that information is stored in a systematic, retrievable format.
Data management software can also enhance search capability, allowing employees to access information quickly. An efficiently organized data system increases organizational effectiveness and enables companies to respond effectively to changes in the marketplace.
Data Security and Compliance Threats
Organizations that handle sensitive information must ensure data security and compliance. Data breaches may occur if appropriate security controls are not implemented in the company.
A data maturity assessment identifies the company’s current security controls and vulnerabilities. Conducting a maturity evaluation allows businesses to safeguard their data assets, build customer trust, and avoid costly security breaches.
Implementing an enterprise data management framework helps businesses bolster their access controls and encryption practices.
An enterprise data management system also grants compliance with regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Siloed Data Creating Inefficiencies
Data silos occur when different departments store and manage data in isolation, resulting in disparate information. Isolation creates inefficiency and mismatched strategies. The data maturity evaluation recognizes siloed data architecture and suggests solutions for seamless data integration.
How to Perform a Data Management Maturity Assessment
I. Define Scope and Objectives
The initial step of a data management maturity assessment is to define the scope and objectives. Organizations must decide which areas of data management, such as governance, security, analytics, and compliance, should be evaluated.
Clear goals ensure that the assessment provides actionable data to enhance the data management system. Businesses should align the assessment with business objectives to derive maximum value.
II. Build a Cross-Functional Team
Because data management affects several departments, having the key stakeholders from IT, finance, marketing, and operations in the evaluation guarantees a balanced review.
A solid enterprise data management system needs cross-functional teams to collaborate on defining pain points and areas for improvement. Involving different departments creates a data-driven decision-making culture.
III. Evaluate Current Data Management Practices
Organizations must assess how data is collected, stored, processed, and used across departments. Identifying inefficiencies in the enterprise data management system helps highlight gaps in governance and security. This step involves reviewing existing data handling procedures and comparing them with industry best practices.
IV. Adopt a Standardized Maturity Model
Several recognized frameworks, including DAMA-DMBOK and CMMI, offer standardized approaches for assessing data management maturity. These models allow organizations to benchmark their current practices against industry best practices, providing helpful reference points for improvement. Selecting the correct maturity model ensures uniform evaluation.
V. Identify Strengths and Weaknesses
Organizations must benchmark their existing data management capacity against best practices. Identifying strengths enables businesses to leverage winning strategies, whereas weaknesses identify areas that must be addressed immediately. Maximizing enterprise data management tools can dramatically improve efficiency and accuracy.
VI. Evaluate Data Security and Quality
Low data quality and poor security introduce serious threats. A data maturity evaluation should validate data accuracy, completeness, consistency, and industry-mandated conformity. A built-in enterprise-class data management framework provides robust defenses against data hazards.
VII. Review Existing Enterprise Data Management Tools
Organizations must decide whether their existing enterprise data management tool satisfies business requirements. Ineffective or outdated tools may slow data accessibility and reliability. Upgrading to new-generation enterprise data management tools improves efficiency, integration, and automation.
VIII. Create an Improvement Roadmap
Based on the assessment findings, companies must develop a roadmap of priority areas for improvement. Prioritizing improvements in data governance, security, and automation maximizes the impact of changes. A strategic plan provides systematic and measurable progress in data management.
IX. Implement Best Practices and Track Progress
Firms must incorporate best practices like data governance policies, automation, and real-time analytics. Ongoing monitoring ensures the enterprise data management framework continues to be effective. Periodic audits and performance reviews enable sustaining improvements.
X. Re-Evaluate and Revise Periodically
Data management is a dynamic process. Organizations must conduct periodic data maturity evaluations to keep their data management system consistent with business requirements. With changes in technologies and regulations, reassessments ensure efficiency and compliance.
Conclusion
Strong data management is key to business success. However, managing data well is not a one-time task. It needs regular checks and improvements.
A data management maturity assessment helps track progress and spot weak areas. It ensures that your enterprise data management system stays effective as your business grows.
By assessing maturity, businesses can refine strategies and stay ahead. A well-managed data system leads to better decisions, smoother operations, and long-term success.