Long gone are the times when businesses could rely on traditional, manual processes to enhance efficiency, foster innovation, and compete effectively. Plus, the scarcity of skilled human resources is another challenge that adversely impacts an organization’s growth. Limited by human capacity and the inherent inefficiencies of manual processes, a productivity crisis gradually surfaces across the organization. Instead, modern problems require modern solutions. This is where automation steps in, not as a replacement for human ingenuity, but as a powerful tool for unlocking exponential business growth.

Automation, which first surfaced in the 1940s, has evolved from a cutting-edge to a well-established technology today. Business process automation, particularly, offers exciting opportunities for companies across the globe in terms of incremental efficiencies, bolstered productivity, and significant cost savings – accelerated digital transformation comes as an added advantage.
Compelling Reasons for Investing in Business Process Automation
Not to be confused with Robotic Process Automation (RPA) or Business Process Management (BPM), Business Process Automation (BPA) primarily minimizes manual intervention. BPM provides a framework for managing and improving business processes, BPA focuses on automating entire workflows, and RPA targets the automation of specific, rule-based tasks. Simply put, companies can automate some parts or overall processes to streamline operations and standardize workflows. BPA is commonly called workflow automation for this reason. Understanding these distinctions helps organizations choose the right approach for their automation and process optimization needs.
Though the list is lengthy, some of the compelling reasons why organizations should consider investing in business process automation are listed below:
1. Optimized Operations
Workflow optimization is one of the primary benefits of automating business processes. As mentioned already, organizations can use BPA to automate specific steps in a process or even the entire process. In either scenario, BPA can determine the most effective way to operate a workflow and execute it efficiently by applying business rules and logic to both structured and unstructured data sets.
2. Enhanced Productivity
Tasks like data entry, invoice processing, report generation, scheduling, email sorting, etc., are non-core but important and eat up valuable time. Such ancillary tasks can be automated using BPA; thereby, freeing up human resources for more strategic initiatives. Automating such repetitive, no-brainer tasks prevent employee burnout and maximizes productivity, which ultimately drives company growth.
3. Cost Savings
By minimizing manual intervention, streamlining operations, and boosting productivity, BPA automatically helps with cost savings. In fact, a recent report from Deloitte states that automation is helping organizations decrease costs by 32% on average.
4. Greater Accuracy
Even with the best intentions, mistakes are inevitable for every employee. While some errors are very insignificant and harmless, others can pose a serious threat to the company. On the other hand, human error can’t occur when business processes are automated. Thus, process automation is a cost-effective and failure-proof way to increase the efficiency and accuracy of the workflow. This is particularly important for industries such as finance, logistics, healthcare, manufacturing, etc.
5. Assured Compliance
Process automation comes as a savior for companies operating in highly regulated industries like financial services and healthcare as it lets them automate the components of their compliance program. Furthermore, automation reduces the possibility of human error, which could compromise compliance, and frees compliance officers to focus on more pressing concerns that can adversely impact the company. Examples of automated workflows include third-party onboarding and complaints analysis.
6. Accelerated Auditing
By using BPA, organizations can automate a variety of auditing processes, including detail testing, internal control testing, and reconciliations; thereby, freeing up auditors’ time for more difficult tasks. By reducing demands on auditor’s time, businesses can streamline the overall process as well as improve audit quality.
7. Increased Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is a crucial point of differentiation in any industry. Enhanced bottom-line efficiency translates to a superior overall customer experience as employees can better focus on customer-centric activities, including one-on-one interactions, responding to requests quickly and more efficiently, ensuring quality services, and more. Remember, customers are more likely to return to a brand where promised standards are met.
Operate Smartly with Process Automation
Transforming Operations: Common Use Cases for Business Process Automation
Though a range of automation solutions are available today, not all work the best for a given scenario. The capabilities of any automation solution may limit its potential applications. Here are some common scenarios where business process automation solutions prove useful:
I. Employee Onboarding
Onboarding new hires is often time-consuming and cumbersome. Organizing induction sessions, gathering employee documents, filling out forms, and assigning mentors are among the many activities HR personnel need to manage on a regular basis. Business process automation simplifies the process, enabling a seamless transition from one activity to the next. It also ensures all the relevant employees have access to the required information and real-time visibility into all stages of the onboarding process.
II. Purchase Orders
Purchase order management is another activity that qualifies as a great candidate for automation. It involves multiple levels of approval and demands highly accurate information. In the absence of automation, the process may become chaotic, leading to delayed approvals, errors in the purchase order, and lower operational efficiency. Business process automation speeds up the authorization of purchase order requests. It also ensures accurate recording of data which can be accessed by the stakeholders whenever required.
III. Customer Service
Answering all customer queries manually may become exhausting for support representatives. It is possible to automate the process where a chatbot sends out standard replies to questions frequently asked by customers. A human agent may be required to intervene only if the query becomes too complex for the chatbot. This eases agents’ workload, enabling them to direct their time and effort on issues that require empathy or brainstorming. Additionally, these bots help serve customers who need assistance outside of regular business hours.
IV. Lead Management
Nurturing leads effectively allows businesses to close deals faster while spending fewer resources. Business process automation streamlines lead management, allowing sales teams to focus on building relationships instead of getting bogged down in mundane tasks. Automated workflows help extract prospect data from forms integrated with the CRM. The data is automatically routed to a suitable salesperson depending on their expertise and availability. Besides, sales teams can schedule follow-up messages to keep the leads interested in their offerings.
V. Finance and Accounting
Traditional methods of using spreadsheets for handling accounting activities such as accounts payable or financial reporting have been found to be notoriously time intensive. Being prone to errors, they may lead to additional overheads and frustration among teams. Business process automation speeds up these processes.
All the incoming invoices undergo an automated approval process which ensures all the stakeholders duly sign them off. The payment is released automatically once the invoice has been approved, enabling timely payment of bills. Likewise, reminders to collect due payments are also automated. BPA thus minimizes human intervention, enabling efficient, cost-effective operations while boosting regulatory compliance.
Identifying the Right Automation Opportunities
Though the potential benefits of business process automation are significant, determining which processes to automate is the ultimate challenge. That said, a process may be a strong candidate for automation if it fits into one or more of the following categories:
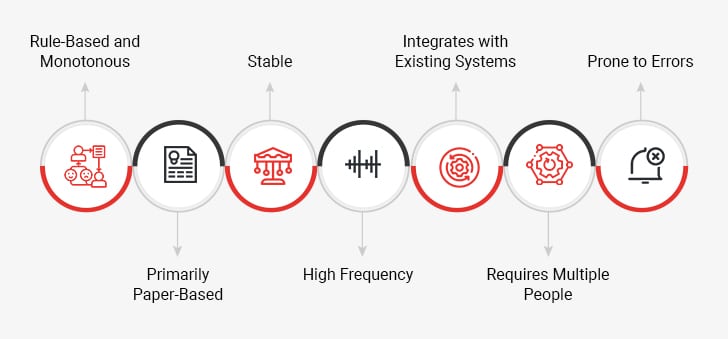
- Rule-Based and Monotonous: Are the rules in the process so well-defined that a software solution can easily follow them?
- Primarily Paper-Based: Does the process involve copious paperwork? Can this process be modified to be performed entirely on computer systems?
- Stable: Do the rules for the process stay the same or do they change frequently?
- High Frequency: Is the process performed frequently enough every day to justify the investments made?
- Integrates with Existing Systems: Can the process be easily integrated with the existing tools, applications, and IT infrastructure?
- Requires Multiple People: Does the process involve many skilled knowledge workers who would be better off working on higher-value tasks?
- Prone to Errors: Does the process involve dealing with sensitive data making it susceptible to errors?
Best Practices for Using Business Process Automation
I. Set Clear Expectations and Goals
Defining goals and expectations serves three main purposes. First, it proves the feasibility of BPA as a business case, which in turn justifies the investment in BPA technology. Secondly, it serves as an endpoint from where stakeholders can develop a strategic plan of action for their business process automation project. Thirdly, it helps in assessing the effectiveness and ROI of BPA project, which brings us to our next recommended practice.
II. Analyzing the Outcomes Achieved
When setting goals for BPA initiatives, specify the metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to monitor the progress. For instance, if a company is trying to save costs or accelerate the time for a business process, then the results should be actively monitored to check if automation is delivering the expected value.
III. Understanding Compliance Requirements
When creating a business process automation strategy, it’s crucial to consider potential needs, constraints, and limitations – regardless of whether a process (or processes) is within or outside the compliance program.
IV. Keeping a Record of Everything
Ensure that every facet of the business process automation strategy is well documented, with access to all the relevant staff, starting with the changes to be implemented and ending with the modifications made to the current workflow. Establishing this single source of truth will help avoid any confusion and ensure that the new procedure is followed consistently.
V. Investing in Staff Training
In addition to outlining the modified duties and responsibilities for staff members and how the new process will operate, training materials should also provide a justification for the change. Encouraging staff members to understand the rationale behind business process automation is a crucial aspect of change enablement, as it enhances the chances of user acceptance and the general prosperity of BPA projects.
VI. Scaling from a Small Start
It is better to identify three to five processes that can benefit from automation and move forward, rather than trying to automate everything at once. In due course, it will become evident whether business process automation produced the desired results based on the objectives and key performance indicators that were established previously. If the BPA initiative is successful, management can scale it up to cover more processes; if not, business leaders can use the gathered information to pinpoint possible weak points and areas for development.
Key Challenges in Implementing Business Process Automation Solutions and How to Overcome Them
While business process automation allows us to tackle many manual, time-consuming operations, it is no silver bullet. Like with any other technology, there are potential downsides that businesses should consider before deciding to implement it.
-
High Initial Investment: Business process automation services incur high upfront investment. The cost of buying new hardware and software and integrating the BPA solution with the existing infrastructure is substantial. Not to mention the expenses associated with training the employees and the disruption happening during the transition.
To mitigate the challenge, it is important for businesses to conduct an in-depth cost-benefit analysis. This will help assess if the solution is capable of generating adequate returns. Additionally, businesses may also consider implementing the BPA solution in phases; this will enable them to spread out costs, minimizing risks.
-
Data Security and Compliance: Automated systems deal with vast amounts of business-critical data, which if not handled properly may lead to breaches and other vulnerabilities. When deploying a BPA solution, it’s vital to ensure seamless accessibility to information while ensuring it doesn’t fall into the hands of malicious entities.
To safeguard sensitive data, businesses need to integrate security into every aspect of business process automation development. Stringent security measures such as role-based user authentication, encryption, and multi-factor authentication should be put in place. Additionally, assessments need to be performed regularly to see if the data is accurate, up-to-date, and compliant with existing regulations.
-
Integration with Existing Systems: Another notable challenge is integrating the business process automation solution with the existing IT infrastructure. Most organizations use legacy applications in their IT ecosystems, which may not communicate effectively with a new tool. This may create data silos, leading to operational bottlenecks.
To enable seamless integration, businesses should select tools that are interoperable with the tools and applications they are currently using. They should also consider using an integration platform to ease the process if required.
-
Resistance to Change: Employees in an organization are accustomed to working with a set of systems or processes. When automation is brought in, they are reluctant to adopt it. While some of them fear job displacement, others are unsure of how the technology would benefit them. Such resistance affects the organization-wide adoption of BPA solutions.
Organizations should establish a comprehensive change management strategy to tackle the challenge. Regular training sessions may be conducted to communicate how the solution will benefit the workforce and how their skills will be utilized post-implementation. Engaging the stakeholders early on and addressing their fears and concerns will help ensure seamless adoption.
Bottom Line
Business process automation is a game-changer for companies trying to improve productivity, increase efficiency, and streamline their operations. Additionally, companies can improve revenue lifecycle efficiency, optimize expenses, and reach higher accuracy levels, which ultimately propel their growth.