Data holds the key to unlocking new opportunities for businesses. Every organization dedicatedly gathers data, as every bit of it can potentially inform a decision or help in uncovering avenues for business expansion. However, mere data collection doesn’t suffice. A business may be inundated with information but may find itself scrambling for answers that matter. Their raw data must be harnessed and transformed into insights, which ultimately trigger actions and fuel decisions.
Nonetheless, the sheer volume, velocity, and variety of data make processing and analysis a difficult task for most companies. They need the right blend of skills and technologies to convert data deluge into tangible business growth, thus creating the need for data engineering. Data engineering builds a foundation where data is accurate, ready to use, and available to everyone, from entry-level staff to top leadership. These solutions lead to quicker decisions and optimize operations across the business. Effective data engineering also ensures that systems can handle growing volumes of data over time.
This blog explains how data engineering boosts business growth by breaking down its key components and describing the benefits it brings to forward-looking companies.
Table of Contents
Understanding Data Engineering and Its Components
How Data Engineering Supports Business Decisions
How Data Engineering Drives Flexibility for Growing Companies
How Data Engineering Strengthens ROI Through Efficiency Improvements?
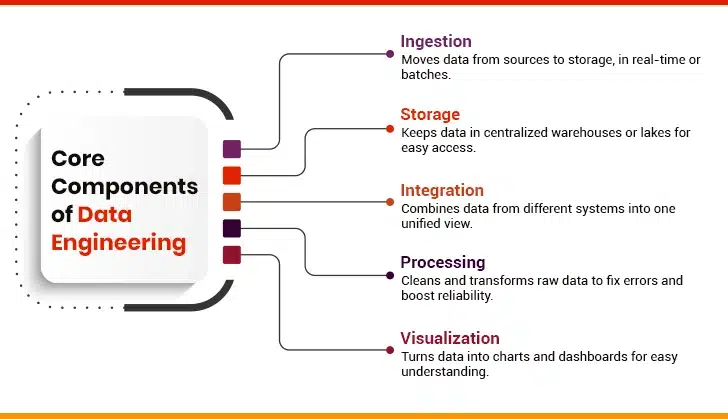
Understanding Data Engineering and Its Components
Data engineering is the practice of designing and developing models and architecture for data collection, storage, and analysis. The main objective of this process is to transform massive quantities of data into strategic insights via processes like data warehousing, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) operations, and data integration. Data engineers create and deploy algorithms, data pipelines, and workflows to sort raw data into ready-to-use formats. This ensures that data is readily available for use by data scientists, data analysts, developers, and other business stakeholders. Through these efforts, data engineering transforms raw, noisy data into a strategic asset that can drive efficiency, innovation, and profitability.
Likewise, data engineering solutions are wide and versatile, offering end-to-end solutions to design, develop, deploy, and maintain systems that collect, cleanse, store, process, analyze, and visualize data using BI tools. Let’s get into the details:
1. Data Ingestion
Data ingestion is the process of moving/replicating data from sources to the cloud storage platform. It is an important step as it determines the type and quality of data used for analysis. Data engineers need to decide whether this process will be carried out in real-time or in batch processing mode. Real-time streaming works uninterruptedly and is vital for time-sensitive tasks like fraud detection. Batch processing gathers data at set times and works well for non-urgent tasks. Teams can combine both approaches by collecting data continuously but processing small batches every couple of minutes.
Modern tools gather information automatically from databases, sensors, logs, and business applications. These tools must balance speed and cost as the influx of data grows.
2. Data Storage
The collected data must be stored in a central database for further processing and analysis. Therefore, data engineers must devise the optimal storage solution so that employees can access the datasets instantly. Companies can choose from on-premises and cloud storage solutions or use a combination of both. The two most popular methods to store big datasets are:
- Data Warehouse – It is a centralized repository where data from various sources is stored, integrated, and managed. Data warehousing facilitates business intelligence activities, generates reports, and allows complex queries to be performed easily by offering a single view of the organization’s data.
- Data Lakes – Designed to store both structured and unstructured data, including text, images, and videos; data lakes differ from data warehouses. Companies can invest in data lake services to store and analyze sheer volumes of data, as well as develop robust data governance frameworks to ensure data quality and compliance.
3. Data Integration
Organizations usually have more than one source of data, such as ERP, CRM, HR systems, etc., which creates silos. Ideally, data from different sources must be combined into a single, unified view to harness its true potential. Thus, data integration helps in breaking data silos and ensures that data is consistent, accurate, and up-to-date across all systems. This comprehensive view of the data provides a clear picture to the business leaders and helps them making informed decisions. For instance, the data warehouse needs to be connected to BI tools and ERP systems to perform analysis and provide data visualizations to the end users.
4. Data Processing
Raw data contains errors and gaps that make analysis difficult. Data processing rectifies these issues through cleaning and transformation. It removes duplicate records, fills missing spots, standardizes formats, and fixes odd values.
Research from IBM tells us that bad data costs businesses in the USA more than $3.1 trillion annually. Proper cleaning of datasets follows a clear path, where teams check data quality, create automated cleaning rules, and keep a watch on the results.
Processing reshapes data to make it more useful. Formatting datasets thoroughly ensures that the final output is reliable and suitable for gathering valuable insights.
5. Data Visualization
After the entire data is processed and analyzed, now is the time to convert the retrieved insights into visual elements that convey complex data relationships in the simplest possible way using BI tools. Data visualization professionals can help businesses identify the right BI tool based on their unique requirements. Tableau and Google Looker Studio help them turn numbers into visual narratives without the need for any technical expertise.
Other than this, the experts also help in setting up the dashboards and integrating them with the existing infrastructure so that employees across the organization can access those visualizations.
Enabling Cutting-Edge Analytics with a Synergy Between Data Engineering and Data Science
How Data Engineering Supports Business Decisions
Quality and timely information drive smart business decisions. Data engineering creates a foundation that helps organizations garner useful insights from their datasets and make better choices. This approach strengthens growth and helps maintain a competitive edge.
I. Real-Time Access to Reliable Data
Present-day businesses cannot fulfill their needs by overnight processing of data. Research tells us that 63% of use cases must process data within minutes to make it work. Data engineering systems address this issue through real-time data processing systems that deliver immediate insights.
These systems detect fraud, optimize supply chains, and manage risk as events happen. Organizations can prevent problems from becoming bigger by processing data in real time. To give an example, financial institutions can spot aberrant transactions and take immediate action to prevent losses.
II. Improved Reporting Across Departments
A “single source of truth” brings various departments on the same page. The result? Marketing and sales avoid arguing over different numbers. This shared foundation keeps the whole company moving in the same direction.
Data engineering uses integration to break down silos that previously trapped information within departments. This allows information to flow freely. Because of this, customer details stay consistent as prospects move between various channels. Besides, it becomes easier for teams to share and discuss new ideas.
III. Quicker Response to Market Changes
How quickly businesses respond in competitive markets often decides their success. Data engineering provides infrastructure that helps businesses forecast market changes instead of reacting to them after they have happened.
Sales and marketing teams can use data analytics engineering solutions to find the best timing for new launches. Retailers can adjust their prices based on demand. Manufacturers can detect production bottlenecks before they impact deliveries. This quick response becomes a huge advantage in markets that change rapidly.
| Benefit | How Data Engineering Helps |
| Real-Time Access to Reliable Data |
Processes data immediately for instant insights. Supports real-time fraud detection, supply chain fixes, and risk management. |
| Improved Reporting Across Departments |
Breaks down silos to create a single source of data. Keeps customer data consistent and aligns departments. |
| Quicker Response to Market Changes |
Provides infrastructure to forecast shifts instead of just reacting. Helps with timely product launches and adjusts prices based on demand. |
How Data Engineering Drives Flexibility for Growing Companies
|
“Data engineering is the backbone that keeps the data world upright. Without it, everything collapses.” – David Linthicum, Cloud and AI Thought Leader and Innovator |
Growing companies need to handle expanding volumes of data while staying ready for new opportunities. Data engineering provides the foundation to achieve both goals.
1. Handling Increasing Data Volumes
Digital information keeps growing at a startling pace. The total amount of data produced will reach massive levels in a few years. Companies, however, save and process only a small fraction of this data. Data engineering solutions solve this problem by using systems that can expand easily to accommodate new data.
Data engineers create modular systems that split pipelines into three parts: ingestion, transformation, and storage. Each component can scale on its own as the business grows. Many companies use cloud services to make these systems more flexible. The cloud adjusts resources to match the load, which avoids high upfront expenses.
2. Supporting New Business Models
With time, businesses need to change their working methods and embrace new models. Their data requirements also shift accordingly. Other than this, many of their applications demand data processing within minutes. Data engineering helps build strong, flexible setups that aid this growth.
Data processing systems help companies set up distributed processing frameworks that scale on their own. Due to this, companies can launch new products and services without rebuilding their entire data system. They can also adjust swiftly to changes in the business environment.
Uncovering the Best Practices for Successful Databricks Lakehouse Migration
3. Adapting to Evolving Data Sources
New data sources appear every few days in the digital world. Data engineering helps build systems that can absorb these new inputs without struggle.
Modern setups can handle unstructured information as smoothly as structured datasets. This is important because messy and unorganized information makes up nearly all the data created today.
Smart companies now adopt data lakehouses that combine the structured querying capabilities of warehouses with the flexibility of data lake services. This helps companies maintain speed while adjusting to new data types and sources.
How Data Engineering Strengthens ROI Through Efficiency Improvements?
Data engineers spend around 10%-30% of their time finding data problems and another 10-30% fixing them. These issues create inefficiencies that properly designed data engineering systems can fix.
I. Reducing Data Handling
Data teams waste resources and make mistakes with manual processes. Automation through data engineering takes over mundane tasks, like moving data and verifying formats. This approach cuts the time spent monitoring and fixing problems when implemented correctly.
Automation creates standardized workflows that keep data clean and reduce the risk of human error. Business teams can then focus on strategic projects. They stop doing tedious jobs that do not add value. All of this helps them get better returns from their data investments.
II. Enabling Data Observability
Analysts regularly grapple with data quality issues, which impede their ability to gather useful insights from their data. This inefficiency results in high costs for organizations. Observability tools in data engineering systems help here by making work much more efficient for these specialists. They can now find and address anomalies and unexpected behaviors in their data almost immediately. With these tools, it has now become possible to spend far less time on troubleshooting. Teams become more productive, get insights much faster from their data, which leads to a much higher ROI.
Conclusion
Data engineering is essential for businesses that aim to extract full value from their data. This specialized field turns scattered data into cohesive resources that accelerate growth across the whole organization. Companies investing in data engineering systems build the foundation needed for smart data analysis and near-instant decision-making abilities. Firms with strong data skills respond faster to market changes. They adopt new ways of working with little effort and cut costs by a considerable amount. Their operations become resilient with flexible systems that grow as data volumes increase.
For growing companies, data engineering is a smart investment, not just a tech expense. Teams with solid data foundations prepare themselves for steady growth while their competitors struggle with fragmented information and slow answers. Proficiency in turning raw information into meaningful insights creates a path to data-driven success.