The advent of innovative technologies has compelled businesses to modernize their IT landscape to realize higher agility, scalability, and cost savings. These may include legacy AS400 or IBM i systems that run mission-critical applications in several industry verticals. While AS400 systems have long been known for their robustness, reliability, and security, they come with limitations-monolithic architecture, 5250-based green screens, and costly OS upgrades,- that may prevent businesses from innovating. Organizations that keep running on such obsolete technologies are unable to sustain themselves in today’s immensely competitive marketplace.

To keep pace with the current IT landscape and breathe new life into monolithic applications, businesses are increasingly considering application modernization services. No wonder, the market for application modernization services is predicted to reach USD 39.62 billion by 2029, growing at a rate of 14.8% between 2024 and 2029. (MarketsandMarkets)
Read this informative piece to understand why AS400 modernization is challenging, how it benefits a business, and what approach should be adopted while modernizing legacy AS400 systems.
Why Modernize Legacy AS400 Systems: AS400 Application Modernization Benefits
Working with old AS400 or IBM i systems may cause a business to run into problems, especially when these systems don’t align with their goals. Legacy systems accumulate bugs and other issues over time and are difficult to integrate with modern technologies.
Modernization of these systems enables businesses to stay competitive in an ever-evolving business environment, pivot with changing customer requirements, and utilize emerging technologies to become more agile and efficient.
Here are the key benefits of AS400 application modernization for enterprises:
1. Reduced Technical Debt
AS400 applications grapple with issues such as bugs, high maintenance costs, and lack of scalability. As a result, organizations are forced to allocate a significant part of their development budget towards mitigating such issues. By strategically modernizing their legacy systems, businesses build robust applications and eliminate spending on the maintenance of outdated code.
2. Improved User Experience
Existing IBM i applications with 5250-based ‘green screens’ are an eyesore for users. Owing to their monolithic architecture, these applications tend to lack flexibility and are hard to make changes to. Application modernization greatly enhances user experience through a transformation of the user interface, integration of new features and services, and automation of manual processes.
3. Higher Productivity
Modern technology reduces the cognitive burden on developers and IT staff, enabling them to work at their full potential. Modernization of legacy apps allows businesses to automate repetitive tasks, allowing businesses to focus on critical, high-value work. Besides, improved functionalities and features of a modernized application further streamline operations.
4. Increased Agility
By modernizing AS400 applications, organizations gain the agility needed to respond quickly to market changes. This flexibility enables companies to adapt their strategies and offerings, helping them stay competitive.
5. Access to New Technologies
Modernization opens the door to new technologies that enhance business operations. Organizations may take advantage of Cloud Computing, Advanced Analytics, and Artificial Intelligence, allowing them to innovate and improve their services.
6. Futureproofing IT Assets
By modernizing AS400 applications, businesses ensure their systems remain relevant. This future-proofing strategy protects investments and prepares organizations for upcoming challenges and opportunities.
7. Increased Revenue
The monolithic nature of their code base makes AS400 applications difficult to modify. In contrast, new features, functions or services are easily integrated into a modernized application. This enables businesses to better serve the needs of their customers, leading to enhanced user experience and improved bottom line.
Reimagine Efficiency with Our AS400 Modernization Solutions
Challenges with AS400 Application Modernization
While modernization comes with its own benefits, it tends to be complex and challenging. Here are some common challenges organizations face while modernizing their IBM I systems:
1. Knowledge Deficit
The biggest hurdle to modernizing AS400 is a shrinking talent pool. In addition to a lack of subject matter experts, the absence of functional and technical documentation, and patchy source code may further overwhelm a team.
2. Lack of a Clear Strategy
IBM I applications may come with millions of lines of code. In the absence of a robust strategy on what to maintain, what to upgrade, and what to migrate, businesses may not realize the desired outcomes.
3. Legacy Code Complexity
AS400 systems often contain complex and monolithic codebases, making it difficult to refactor and modernize applications without disrupting core functionalities.
4. Data Migration
Modernization involves the migration of massive amounts of data present across disparate databases and files. Additionally, most IBM I systems use EBCDIC character encoding, while modern systems operate on ASCII encoding.
5. Legacy System Dependencies
Many AS400 applications rely on outdated hardware and software, making integration with modern systems difficult and limiting overall interoperability.
6. Resistance to Change
Notwithstanding the digital disruption happening everywhere, employees prefer continuing with obsolete systems to migrating to modern ones. Organizations face stiff resistance from key stakeholders whenever a major overhaul occurs.
7. High Cost of Modernization
High initial costs may deter an organization from making the leap to the cloud. Estimating the budget for modernizing AS400 is tricky as businesses may need to accommodate several unforeseen expenses down the line e.g. scaling the workforce.
8. Impact on BAU
The cutover may be accompanied by a long downtime due to the high complexity of AS400 systems as well as modifications in the source code during bug fixes or enhancements. Plus, the user interface of the application would change considerably, resulting in reduced user productivity for at least a few days.
9. Compliance Challenges
Ensuring that modernized AS400 applications meet current regulatory standards may be challenging, especially when dealing with sensitive data and evolving compliance requirements.
Leading Business Realized 35% Jump in Efficiency with a Revamped WMS
Best Practices for Modernizing an AS400 Application
Modernizing a legacy AS400 application requires adhering to a structured approach. Below are the best practices that need to be followed in order to ensure a successful modernization.
I. Assess the Current State of AS400 Systems
Assessing the existing legacy system is a great starting point. Engage AS400 experts to perform a comprehensive analysis to identify the challenges faced by system users and areas for improvement. The assessment needs to be systematic and detailed, covering all facets of the legacy system—functional aspects, infrastructural environment, technical specification, dependency on third-party APIs, database management procedures, and security measures.
II. Identify the Problems and Define Goals
This is a critical step when embarking on a modernization journey. By examining different aspects of the system, businesses get a clear picture of their problems and pinpoint areas for improvement. Accordingly, they devise a well-thought-out modernization strategy and establish realistic goals for the short as well as long term.
III. Analyze and Select a Suitable Modernization Approach
Once the problem and goals have been defined, it’s time to decide how the application will be updated. There are several common approaches to modernization differing in complexity, cost, risk, and overall impact. Businesses may choose any depending on their requirements, goals, and limitations.
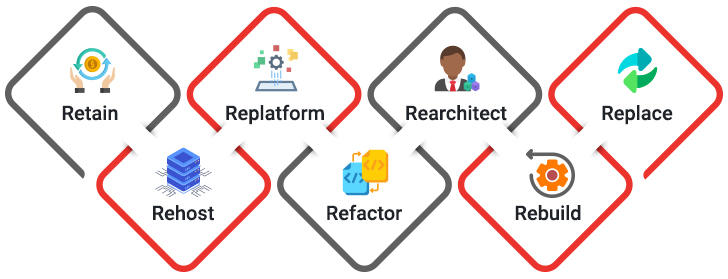
a. Retain
This is a low-risk approach where components of the AS400 application are retained within a new architecture. APIs are built to connect the legacy application with modern elements in the system.
b. Rehost
Also called the ‘lift and shift’ approach, rehosting involves the deployment of legacy IBM I components to another environment (physical, virtual, or cloud) with little to no code modification. Rehosting is fast, easy to implement and establishes a solid foundation for gradual changes down the line.
c. Replatform
The application’s components are moved to a new runtime platform while keeping intact the code structure and features and functions of the system. With replatforming, organizations realize improved performance with minimal effort.
d. Refactor
The code is restructured and optimized to reduce technical debt. Refactoring involves a few modifications on the back end with no major changes to the front end or the functionality offered.
e. Rearchitect
The code is significantly changed and shifted to a new architecture with enhanced capabilities. This approach reduces the total cost of ownership (TCO), while improving application resilience and agility.
f. Rebuild
The most expensive option, a full rebuild, involves rewriting the AS400 application from scratch without changing the scope or specifications. This approach is adopted to achieve modernization in a phased manner wherein the most critical components may be built and deployed first, followed by the rest of the components until the entire application has been transformed.
g. Replace
The legacy AS400 system is scrapped and replaced with an entirely new system that meets business needs. Commonly achieved through SaaS platforms, this option entails a significant amount of planning on how the data will be migrated to the new system or how to minimize disruption during the changeover.
IV. Choose a Trusted AS400 Modernization Partner
Modernization of AS400 systems is a niche skill, so it’s highly unlikely for the internal teams to have the requisite skills or resources to decide on the right modernization approach or cloud service.
Partnering with a reliable AS400 application modernization company enables a business to achieve a frictionless transition. It’s advisable to look for a technology partner with extensive experience in legacy application modernization and proven capabilities in re-engineering technology and systems. To maximize returns on your tech investment, choose an AS400 team specialized in DevOps and Agile methodologies.
V. Observe and Optimize as Needed
Once the modernization project kickstarts, it’s imperative that the changes made are iteratively tested and optimized in order to make sure there are no issues in the hosting, databases, or connectivity to other services. Continuous improvement allows the application to adapt to changing user demands.
Closing Thoughts
Irrespective of the approach chosen, AS400 modernization is a complex, time-consuming, and labor-intensive endeavor. With that said, the results are worth the effort, provided the right strategy is followed.
At Damco, we handle every aspect of IBM i modernization-from assessing your existing solution and devising a robust modernization strategy to rebuilding your application from the ground up and providing post-modernization support. If you want an experienced IBM i modernization company to revive your age-old systems, reach out to our AS400 experts.





