Picture this: a team of digital wizards working behind the scenes, crunching numbers, fine-tuning every customer touchpoint, and taking your business to newer levels of productivity. This isn’t some far-off fantasy—it is what AI agents are doing in the business world.

Think of them as your digital dream team, working round the clock to give your business the much-sought-out competitive edge. They are surfacing insights you never knew existed. They are refining customer experiences with the precision of a master craftsman. In short, they are changing how businesses operate from the ground up, making moves that would have seemed impossible just a few years ago.
Table of Contents
What are AI Agents-A Quick Recapitulation
- Simple Reflex Agents
- Model-Based Reflex Agents
- Goal-Based Agents
- Utility-Based Agents
- Learning Agents
- Multi-Agent Systems
- Hierarchical Agents
How are AI Agents Reshaping Businesses: Use Cases
- Customer Service
- Lead Generation
- Recruitment
- Supply Chain
- Cybersecurity
- Financial Reporting
- Project Management
The Final Word
What Are AI Agents: A Quick Overview
Simply put, AI agents are computer programs that can perform tasks by making decisions based on their inputs, goals, and the environment. Unlike conventional automation software that is programmed to follow a set of rules, these agents can learn, adapt, and act autonomously.
AI agents implement an action with the best possible outcome after considering their past as well as current perceptual inputs. They act in their environment which may or may not have other agents. They perceive the environment through sensors and respond to that environment through actuators.
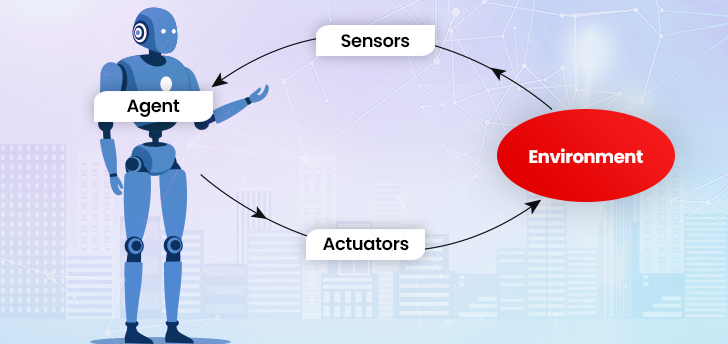
Their ability to continuously learn from each interaction with their environment makes them invaluable in decision-making and strategic planning.
Types of AI Agents
When we explore the world of AI agents, it reveals a diverse array, each with its distinct functionalities and applications. Picking the right type of agent for your business function can make all the difference.
1. Simple Reflex Agents
Simple reflex agents operate on a simple condition-action rule. If the condition is fulfilled, action will be taken, otherwise not. They act only on the basis of their current perception and ignore the historical data. As a result, they prove effective only in highly structured environments.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
These agents have an internal world model, so their responses are based on their current perception as well as the internal model. They can track aspects of their environment that may not be immediately perceptible. As a result, they operate effectively in partially observable environments too.
3. Goal-Based Agents
These agents represent a significant leap in AI, as they operate with a clear goal, and their every action is intended to take them closer to their goals. Such a forward-thinking capability allows them to navigate complicated scenarios with ease, making them suitable for high-level decision-making.
4. Utility-Based Agents
Utility-based agents represent a more sophisticated approach to decision-making, as they are employed in situations where multiple outcomes are possible. They also aim to achieve a goal as goal-based agents do, but they choose the course that maximizes the expected utility (preference).
5. Learning Agents
As the name indicates, learning agents learn from their past experiences and enhance their performance with time. These agents are suited for complex, evolving environments where they become increasingly effective in decision-making by continuously integrating feedback.
6. Multi-Agent Systems
In this system, multiple AI agents work in coordination to achieve a common goal. These systems are used in complex scenarios where different agents handle different aspects of a process, e.g., supply chain management.
7. Hierarchical Agents
Here, several agents are organized in a hierarchy and higher-level agents supervise the actions of lower-level agents. While higher-level agents establish goals and constraints, the lower-level ones execute specific tasks. These agents prove beneficial in environments where tasks need to be broken down and managed at several levels.
AI Agents for Businesses: Top Use Cases
I. Customer Service
Today, when customer expectations are at an all-time high, no business can afford to have below-par customer support. This is corroborated by a recent Salesforce study where 80% of users consider customer experience to be as important as an organization’s product/service. And AI agents shine when it comes to delivering high-quality service—they help users find the right product, troubleshoot issues, assist with checkouts, and much more.
Sophisticated AI agents learn on their own; they leverage historical data to predict customer needs and preferences and even flag potential issues before they become conspicuous. Most of these agents use natural language processing (NLP) to analyze text and speech and study customer sentiment. So, if a customer feels frustrated or irate, the agents sense it immediately and tweak their approach, making the interaction sound empathetic.
II. Lead Generation
65% of businesses say lead generation is their biggest priority. AI agents help sales and marketing departments automate several aspects of the lead generation process. From capturing new leads to converting leads into prospects, these agents are being strategically used to shorten the sales cycle and maximize ROI.
When integrated with technologies such as conversational AI and machine learning, AI agents allow businesses to analyze vital metrics such as customer buying history and cart abandonment rate. This way, they spot performance bottlenecks that may have led to lower conversions. Businesses can also deploy AI agents to examine sales calls and outreach emails, which can then be fine-tuned.
AI-based predictive analytics helps figure out which prospects are most likely to convert, based on their past interactions, behavior, and demographics. This allows businesses to focus their effort on the most promising leads and achieve a higher ROI on their spending.
III. Recruitment
Recruiting the right candidate for a role is a time-intensive process. In fact, the average recruiter spends around 30 hours every week on activities such as sourcing candidates, screening job applications, arranging interviews, and collaborating with other team members.
AI agents simplify all these aspects of recruitment. They can search through job sites, internal databases, and social media channels to identify and source the best-fit candidates for any position. AI-based assessment tools are used by organizations to assess a candidate’s skills, professional competence, and cultural fit. HR teams further gather data from these tools to analyze a candidate’s strengths, weaknesses, and overall personality.
With AI, it has become easier for HR personnel to provide an engaging and personalized onboarding experience for new hires. This creates a positive first impression and paves the way for a successful employer-employee association.
Drive 10x Productivity with Autonomous AI Agents
IV. Supply Chain
As their complexity and interconnectedness continue to grow, supply chains have become more fragile. Organizations are increasingly using AI-based solutions to minimize human intervention and make supply chains more efficient and resilient.
Manufacturing companies utilize AI agents to manage their inventory levels with enhanced precision and efficiency. Equipped with the ability to handle large swathes of data, AI agents forecast demand in a timely manner. Advanced AI agents even predict unforeseen shifts in demand after factoring in market trends, economic scenarios, and seasonal fluctuations. This helps businesses prevent incidences of understocking and stock-outs.
AI-powered agents help create more efficient warehouses by assisting with their layouts. By assessing the amount of material transported through aisles, these agents can recommend the most optimal floor layout that minimizes inventory travel time and maximizes its accessibility through all stages. They also help decide the most suitable routes for workers, leading to reduced congestion and improved fulfillment rates.
V. Cybersecurity
As cyber threats continue to rise in both volume and sophistication, integrating AI into cybersecurity strategy has become important for all organizations. The market for AI in cybersecurity is also growing in response—it is estimated to reach a staggering $102 billion by 2032.
One of the most promising use cases of AI agents is advanced threat detection. Their powerful algorithms analyze large volumes of data to pinpoint anomalies and potential threats in real time. Such an approach allows for timely detection of even previously unseen attacks.
AI agents continually learn from past data and evolve their algorithms to stay ahead of emerging threats. Such flexibility becomes invaluable in maintaining a robust defense in a dynamic threat landscape. Advanced AI agents also help minimize false positives in security alerts.
VI. Financial Reporting
Traditional financial reporting processes are time-consuming and labor-intensive. Finance professionals need to source the right data, check it for accuracy, fit the data into the report, and keep their data compliant with the latest regulations-and a lot more. To streamline these activities, a majority of financial organizations are turning to AI.
AI agents excel at automating tasks such as data entry, reconciliation, and review. This provides auditors with accurate data. They don’t need to spend hours analyzing financial statements and balance sheets. This also allows auditors to focus on high-value tasks such as financial planning and risk assessment.
Another compelling use case of AI agents is financial forecasting. As AI agents learn from past behavior, they can scrutinize financial statements, press releases, and the macroeconomic outlook to detect upcoming trends and risks well in advance. AI also proves helpful in financial planning, as businesses can anticipate future scenarios with precision.
VII. Project Management
Project management teams face many challenges, due to a lack of qualified talent, insufficient planning, and inadequate coordination. Around 44% of the project managers cite a lack of resources as a significant hurdle. Integrating AI into project management processes enables businesses to mitigate these issues and achieve the required levels of efficiency and accuracy across critical functions.
For example, AI agents can analyze historical data along with existing project variables to accurately forecast project outcomes and spot potential risks, allowing for proactive risk management.
AI agents also help project managers with optimal resource allocation, after considering both immediate project needs and anticipated future requirements. This makes sure each project is staffed with an appropriately skilled workforce throughout its lifecycle.
AI agents also generate detailed, actionable project execution roadmaps after a thorough analysis of project goals, ethical considerations, and established deadlines. The resulting blueprint provides clear, strategic guidelines for project implementation.
The Final Word
AI agents are reshaping the business landscape across multiple domains, from customer service to cybersecurity. Their ability to learn, adapt, and make autonomous decisions has helped businesses achieve new levels of efficiency and innovation. While the potential of AI agents is immense, their successful implementation requires careful selection of the right type of agent for specific business needs. As we’ve seen from these AI agents use cases, organizations that strategically deploy these agents are not just optimizing operations but gaining an edge in today’s competitive markets.





